The low-carb diet and the keto diet are sometimes used interchangeably, but they are very different. Broadly speaking, they are both low in carbs and purposely high in fat, while including a high-protein approach as well. However, they do have 3 main differences that set them apart so keep on reading!
Key Differences between Keto and Low-carb
Before we dive into the key differences, and simply to refresh your minds about how these two diets were introduced. The ketogenic diet was originally introduced in the 1920s as a therapeutic approach to manage epilepsy. The low-carb diet gained popularity in the late 20th century driven by the Atkins' diet which was a method to lose weight, improve metabolic health and lower blood sugar levels. They were both initiated to address specific health issues but have since evolved to become popular lifestyle choices for their various health benefits.
Let’s review the main differences between standard keto and low-carb.
1. Macronutrient Composition
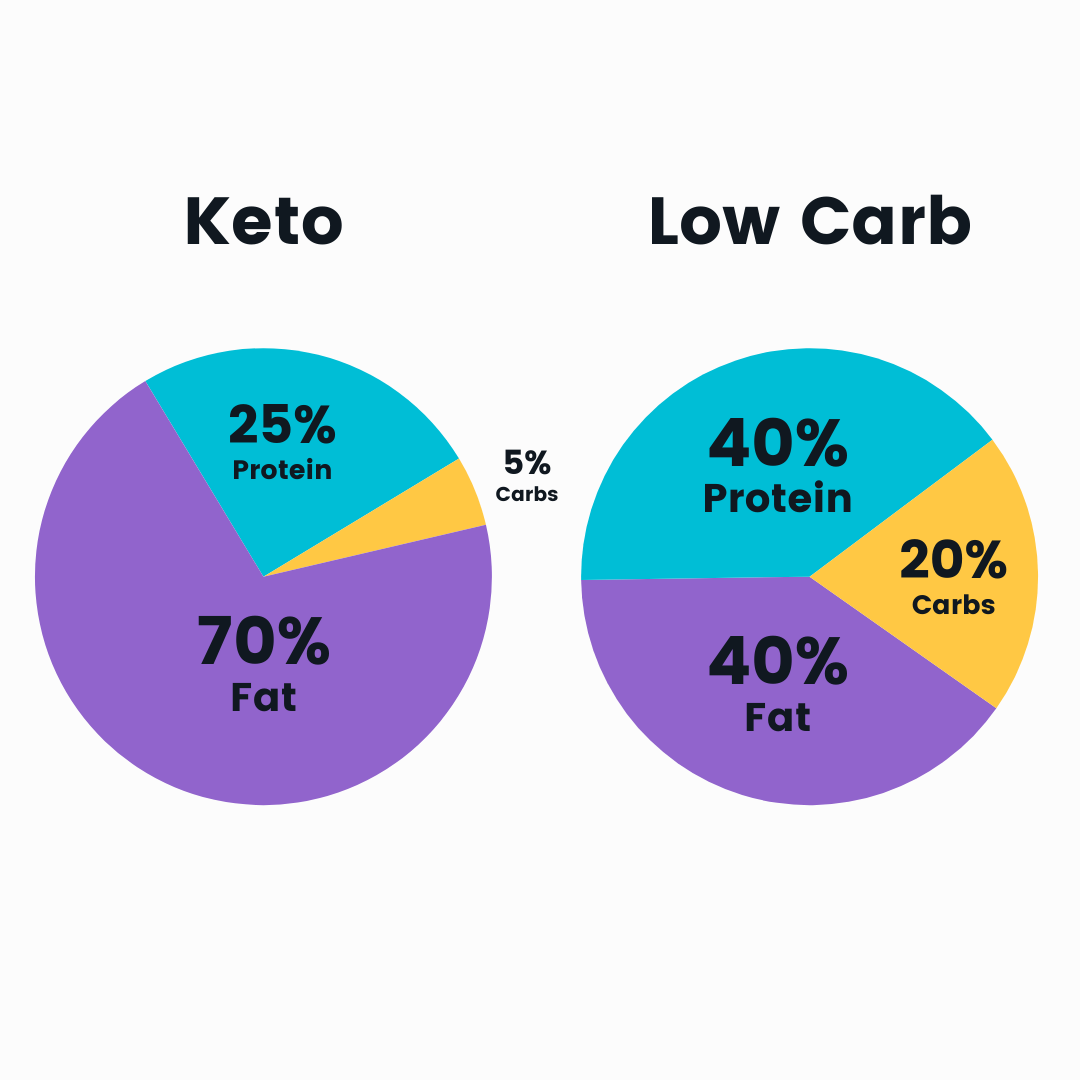
The keto (or ketogenic diet) - 5-10% carbs | 20-25% protein | 70-75% fat
The 5-10% carb limit normally means consuming less than 50 grams of carbs per day. This quantity is necessary to induce a state of ketosis, where the body burns fat for fuel instead of carbs.
In the keto diet, too much protein can be converted into glucose through gluconeogenesis, which can prevent ketosis.
Low-carb: 50-150g carbs | moderate or high protein | varies on fat
The main goal is to focus on protein and to reduce carb intake compared to a standard diet, but not necessarily to enter ketosis. By reducing the quantity of carbs the overall quantity of calories is also cut and the body aims to burn through the glucose more quickly and then starts burning fat for fuel.
Another thing to take into account is that low-carb focuses more on non-starchy vegetables which we'll see further on how they benefit our health.

2. Metabolic state
The metabolic state of each diet is also one of the key differences. The ketogenic diet aims to achieve and maintain ketosis, a metabolic state where the body burns fat for energy instead of carbs, as we’ve previously mentioned. This state is measured through blood, breath, or urine tests.
However, the low-carb diet does not aim for ketosis. The goal is simply to lower carb intake to improve health, aid weight loss, and stabilise blood sugar levels, without the strict requirement of entering a specific metabolic state.
3. Flexibility
While they're both more "restricting" in carbs if you compare it to what our culture has been used to for many decades, the Keto diet is more rigid when it comes to limiting the carb intake. This is mainly because otherwise, the body would not be able to enter or stay in ketosis.
Low-carb on the other hand, allows for a wider variety of foods.
Benefits of Each Diet
Both of these diets have some similar benefits and then some specific ones to each diet.
1. Weight loss
Both diets are proven to be effective for weight loss. Although the keto diet can lead to rapid and significant weight loss in the initial stages, due to the body’s use of stored fat for energy in the absence of carbs, the low-carb diet may be easier to maintain long-term since it’s way less restrictive.
2. Improved blood sugar and insulin levels
By reducing and/or minimising carbohydrate intake, both diets help stabilise blood sugar and insulin levels, which can be very beneficial for individuals with type 2 diabetes, insulin resistance, or pre-diabetes.
3. Increased mental clarity and focus
Plenty of people following the keto diet have reported improved cognitive function and mental clarity. This may be due to the steady supply of ketones, a more efficient fuel source for the brain, and reduced blood sugar fluctuations.
With the low-carb diet you can also experience better mental clarity and focus.
4. Improved energy levels
Most people notice an improvement of their energy levels when starting a ketogenic or a low-carb diet. This is because blood sugar levels are stabilised, which means that there are not that many blood sugar fluctuations or glucose spikes, so they have a steady energy all day long, without spikes and crushes.
Which Diet is Right for You?
To decide which diet is more suitable to you, you need to consider things such as your specific health goals, lifestyle, and dietary preferences.
You probably will need to make a lifestyle change, so keep in mind that when trying to decide, think about your daily routine, social life, and how easily you can stick to the diet in various situations. Also an important part of a diet, are the personal preferences. Your food preferences and aversions play a crucial role. Since both diets restrict certain food groups, it’s important to choose one that aligns with your tastes and lifestyle.
For example, if you are looking for quick weight loss and can adhere to a highly restrictive eating plan, the keto diet may be suitable for you then, since the state of ketosis can accelerate fat burning. However, if you prefer a more flexible and sustainable eating plan, a low-carb diet might be better since it allows for a wider variety of foods and is easier to maintain over the long term. The low-carb diet is way more sustainable, since it’s more balanced, way more permissive and it can easily become a lifestyle that you’ll adopt and stick with it without difficulties.
If you want to try a keto diet or low-carb diet we recommend you to consult with a registered dietitian to help you get started and plan your meals properly so you have no nutrient deficiencies. It will also help you get personalised guidance based on your individual goals, needs, and health status.




Laat een reactie achter
Alle reacties worden gemodereerd voordat ze worden gepubliceerd.
Deze site wordt beschermd door hCaptcha en het privacybeleid en de servicevoorwaarden van hCaptcha zijn van toepassing.